- 常见的分布式应用架构风格:
- 分布式对象(Distributed Objects,简称 DO),架构实例有 CORBA、RMI、EJB、DCOM、.NET Remoting 等
- 远程过程调用(Remote Procedure Call,简称 RPC),架构实例有 SOAP、XML-RPC、Hessian/Flash AMF、DWR 等
- 表述性状态转移(Representational State Transfer,简称 REST),架构实例有 HTTP、WebDAV
在实时性要求很高的应用中,REST 的表现不如 RPC
# REST 概念
- REST(Representational State Transfer):表述性状态转移,Web 应用架构设计指导原则
- 使用 REST 作为指导原则设计的 URI(统一资源标识符)特点是:该 URI 只体现资源(resource)的具体位置,不体现资源的表现形式(Representation),也不体现资源的状态转变(State Transfer),而是通过在 HTTP 请求的头信息中用 Accept 和 Content-Type 字段指定资源的表现形式,通过 HTTP/1.1 协议定义的操作资源的统一接口(Uniform Interface)来对资源执行各种操作
- RESTful 风格:符合 REST 原则的应用程序或设计
- 常见的 RESTful 开发框架:jersey、play、SpringMVC
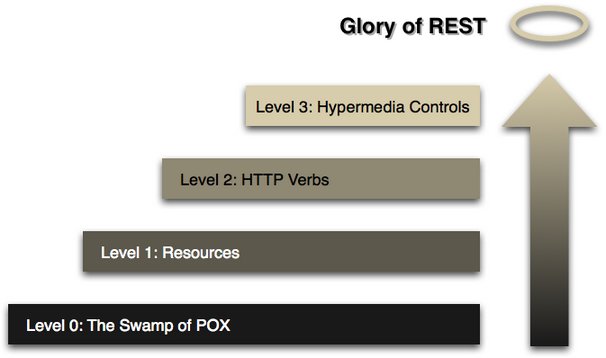
# REST 优点
- 可以利用缓存 Cache 来提高相应速度
- 通信本身的无状态性可以让不同的服务器处理一系列请求中的不同请求,提高服务器可扩展性
- 浏览器即可作为客户端,简化软件需求
- 相对于其他叠加在 HTTP 协议之上的机制,REST 的软件依赖性更小
- 不需要额外的资源发现机制
- 在软件技术演进中长期的兼容性更好
# 统一接口(以 HTTP1.1 协议)
# 7 个 HTTP 方法
- GET(SELECT):从服务器取出资源(一项或多项),返回资源对象的列表(数组)或单个资源对象
- POST(CREATE):在服务器新建一个资源,返回新生成的资源对象
- PUT(UPDATE):在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变后的完整资源),返回完整的资源对象
- PATCH(UPDATE):在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变的属性【补丁】),返回完整的资源对象
- DELETE(DELETE):从服务器删除资源,返回一个空文档
- HEAD:获得一个资源的元数据,比如一个资源的 hash 值或者最后修改日期
- OPTIONS:获得客户端针对一个资源能够实施的操作
# HTTP 头信息(可自定义)
- Accept:代表发送端(客户端)希望接受的数据类型,
- Content-Type:代表发送端(客户端或服务器)发送的实体数据的数据类型
# HTTP 响应状态代码 (opens new window)(可自定义)
- 200 OK - [GET]:服务器成功返回用户请求的数据
- 201 CREATED - [POST/PUT/PATCH]:用户新建或修改数据成功
- 202 Accepted - [ * ]:表示一个请求已经进入后台排队(异步任务)
- 204 NO CONTENT - [DELETE]:用户删除数据成功
- 301 Moved Permanently:被请求的资源已永久移动到新位置
- 302 Found:请求的资源现在临时从不同的 URI 响应请求
- 307 Temporary Redirect:请求的资源现在临时从不同的 URI 响应请求
- 400 INVALID REQUEST - [POST/PUT/PATCH]:用户发出的请求有错误,服务器没有进行新建或修改数据的操作,该操作是幂等的
- 401 Unauthorized - [ * ]:表示用户没有权限(令牌、用户名、密码错误)
- 403 Forbidden - [ * ] 表示用户得到授权(与 401 错误相对),但是访问是被禁止的
- 404 NOT FOUND - [ * ]:用户发出的请求针对的是不存在的记录,服务器没有进行操作,该操作是幂等的
- 406 Not Acceptable - [GET]:用户请求的格式不可得(比如用户请求 JSON 格式,但是只有 XML 格式)
- 410 Gone - [GET]:用户请求的资源被永久删除,且不会再得到的。
- 422 Unprocesable entity - [POST/PUT/PATCH] 当创建一个对象时,发生一个验证错误
- 500 INTERNAL SERVER ERROR - [ * ]:服务器发生错误,用户将无法判断发出的请求是否成功
# 实现 Restful Web Service
- 识别资源:能用 CRUD 操作的名词、将资源组织为集合、将资源合并为复合资源、计算或处理函数
- 选择合适的资源粒度:网络效率、表述的多少、客户端的易用程度;可缓存性、修改频率、可变性
- 设计 URI:
- 使用域及子域对资源进行合理的分组或划分
- 在 URI 的路径部分使用斜杠分隔符 ( / ) 来表示资源之间的层次关系
- 在 URI 的路径部分使用逗号 ( , ) 和分号 ( ; ) 来表示非层次元素
- 使用连字符 ( - ) 和下划线 ( _ ) 来改善长路径中名称的可读性
- 在 URI 的查询部分使用“与”符号 ( & ) 来分隔参数
- 在 URI 中避免出现文件扩展名- 选择合适的 HTTP 方法和返回码
- 设计资源的表述:JSON、XML、HTML、ProtoBuf
# Hypermedia API
- HATEOAS 是 Hypertext As The Engine Of Application State 的缩写
- 采用 Hypermedia 的 API 在响应(response)中除了返回资源(resource)本身外,还会额外返回一组 Link。这组 Link 描述了对于该资源,消费者(consumer)接下来可以做什么以及怎么做
# 使用 Spring MVC 开发 RESTful 服务
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/jobs")
public class JobController{
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String list(){}
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET}
public String get(@PathVariable Long id){}
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(Job job){}
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT}
public String update(@PathVariable Long id, Job job){}
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE}
public String delete(@PathVariable Long id){}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 生成 API 文档
# 使用 Springfox 集成 Swagger2
Springfox 项目目前已经停止维护
# 集成 Swagger2
添加依赖:springfox:springfox-swagger2、springfox:springfox-swagger-ui
配置 Swagger2
@EnableSwagger2 @Configuration public class Swagger2 { @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.forezp.controller")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("SpringBoot 利用 Swagger2 构建 API 文档") .description("简单优雅的 RESTful 风格") .termsOfServiceUrl("http://example.com/rest") .version("1.0") .build(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22访问 /v2/api-docs
添加视图解释器,使用 Swagger UI(Spring Boot 中无须此操作)
@Component public class SwaggerMvcConfigurerAdapter extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addResourceHandler("swagger-ui.html").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/"); registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8访问 /swagger-ui.html
# Swagger2 常用注解
- @Api:修饰类,表示这个类是 Swagger 的文档资源,属性:value url 的路径值,description 对 API 资源的描述
- @ApiOperation:修饰方法,表示一个 HTTP 请求的操作,属性:value 用于方法描述,notes 用于提示内容
- @ApiResponses、@ApiResponse:修饰方法,表示请求的响应信息,属性:code 响应码(可自定义),message 状态码对应的响应信息
- @ApiImplicitParams、@ApiImplicitParam:修饰方法,表示请求参数说明
- @ApiParam:修饰参数,表示对参数添加元数据,属性:name 参数名,value 参数说明,required 是否必填
- @ApiModel:修饰类,表示对实体类进行说明,属性:value 表示对象名,description 描述
- @ApiModelProperty:修饰方法、字段,表示对 model 属性的说明或者数据操作更改,属性:value 字段说明,name 重写属性名字,dataType 重写属性类型(全限定类名),required 是否必填,example 举例说明,hidden 隐藏
- @ApiIgnore:修饰类、方法、参数,可以不被 Swagger 显示在页面上
# 使用 Springdoc 集成 Swagger3
添加依赖:org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui
# REST Clients
# RestTemplate (opens new window)
- Spring 提供的用于访问 Web 服务器端 RESTful 服务的客户端
# 定制 RestTemplate
- 创建请求的通用接口:ClientHttpRequestFactory
- 默认使用的实现类:SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory(uses standard JDK facilities,即 URLConnection)(没有连接池,保持长连接)
- 支持的 HTTP 库:
- HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(Apache HttpComponents (opens new window))
- Netty4ClientHttpRequestFactory(Netty,已过时)
- OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory(OkHttp)
- 优底层请求策略:
- 连接管理:PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager、ConnectionKeepAliveStrategy(默认实现类 DefaultConnectionKeepAliveStrategy )
- 超时设置:connectTimeout、readTimeout
- SSL 校验:证书检查策略(SkipSslVerificationHttpRequestFactory)
- RestTemplateCustomizer
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(RestTemplateBuilder restTemplateBuilder) {
RestTemplate restTemplate = restTemplateBuilder
.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.requestFactory(this::requestFactory)
// 添加自定义的拦截器(implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor)
// .additionalInterceptors(new MyInterceptor())
// 添加日志拦截器(此时需要通过 BufferingClientHttpRequestFactory 缓存 body)
// .requestFactory(() -> new BufferingClientHttpRequestFactory(clientHttpRequestFactory))
// .additionalInterceptors(new HttpLoggingInterceptor())
// 设置 ErrorHandler(extends DefaultResponseErrorHandler)
// 默认的异常处理器是 DefaultResponseErrorHandler
// .errorHandler(new MyResponseErrorHandler())
.build();
// 通过 RestTemplateAutoConfiguration.restTemplateBuilder 自动配置 restTemplateBuilder 时不用以下设置
// HttpMessageConverters#getCombinedConverters
/*
// RestTemplate 的默认构造方法初始化的 StringHttpMessageConverter 的默认字符集是 ISO-8859-1
// RestTemplateBuilder#additionalMessageConverters,在构建器上配置的所有转换器将替换 RestTemplate 的默认 MessageConverter
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().forEach(converter -> {
if(converter instanceof StringHttpMessageConverter) {
((StringHttpMessageConverter) converter).setDefaultCharset(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
});*/
return restTemplate;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// 日志拦截器
@Slf4j
public class HttpLoggingInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
traceRequest(request, body);
long start = System.nanoTime();
ClientHttpResponse response = execution.execute(request, body);
long elapsedTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - start);
traceResponse(response, elapsedTime);
return response;
}
private void traceRequest(HttpRequest request, byte[] body) {
log.info("---> {} {}", request.getMethod(), request.getURI());
boolean isMultipart = false;
for (String field : request.getHeaders().keySet()) {
for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(request.getHeaders(), field)) {
isMultipart = isMultipart || HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE.equals(field) && MediaType.parseMediaType(value).includes(MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA);
log.info("{}: {}", field, value);
}
}
int bodyLength = 0;
if (body != null) {
bodyLength = body.length;
String bodyText = new String(body, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
log.info(""); // CRLF
log.info("{}", isMultipart ? "include binary data" : bodyText);
}
log.info("---> END HTTP ({}-byte body)", bodyLength);
}
private void traceResponse(ClientHttpResponse response, long elapsedTime) throws IOException {
log.info("<--- {} ({}ms)", response.getStatusCode(), elapsedTime);
for (String field : response.getHeaders().keySet()) {
for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(response.getHeaders(), field)) {
log.info("{}: {}", field, value);
}
}
MediaType contentType = response.getHeaders().getContentType();
Charset charset = contentType != null ? contentType.getCharset() : null;
log.info(""); // CRLF
byte[] bodyData = StreamUtils.copyToByteArray(response.getBody()); // 复制流后需保持打开状态
int bodyLength = bodyData.length;
log.info("{}", charset == null ? "May be binary data" : new String(bodyData, charset));
log.info("<--- END HTTP ({}-byte body)", bodyLength);
}
private static List<String> valuesOrEmpty(Map<String, List<String>> map, String key) {
return map.containsKey(key) && map.get(key) != null ? map.get(key) : Collections.emptyList();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
// 休眠时间随次数呈指数递增,ExponentialBackOffPolicy
long interval = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(2);
long maxInterval = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(30);
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
// ...
try {
long sleep = interval;
if (sleep > maxInterval) {
sleep = maxInterval;
} else {
interval = (long) (interval * 1.1);
}
Thread.sleep(sleep);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("{}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 使用 Apache HttpComponents
// client.key-store=classpath:apiclient_cert.p12 # PKCS12 格式证书文件
// client.key-pass=123456 # keystore 密码
// security.key-store=classpath:apiserver.keystore # JKS 类型
// security.key-pass=123456
@Value("${client.key-store}")
private Resource clientKeyStore; // 客户端证书
@Value("${client.key-pass}")
private String clientKeyStorePassword;
@Value("${security.key-store}")
private Resource keyStore; // 信任库
@Value("${security.key-pass}")
private String keyPass;
@Bean
public HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory() {
// 连接池配置
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager connectionManager = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
connectionManager.setMaxTotal(200); // 设置连接池最大连接数(所有主机整体最大并发)
connectionManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20); // 同一个主机/域名的最大并发请求数
SSLContext sslContext = null;
try {
sslContext = SSLContexts.custom().loadTrustMaterial(TrustAllStrategy.INSTANCE).build(); // 信任所有 SSL 证书
// sslContext = SSLContextBuilder.create()
// 设置证书位置及密码
// .loadTrustMaterial(keyStore.getURL(), keyPass.toCharArray())
// 信任所有 SSL 证书
// .loadTrustMaterial(null, (certificate, authType) -> true)
// .build();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Exception occurred while creating SSLContext.", e);
}
// SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext, NoopHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE);
// RequestConfig defaultRequestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
// .setConnectTimeout(2000) // 设置连接超时时间
// .setSocketTimeout(5000) // 请求获取数据的超时时间
// .setRedirectsEnabled(true)
// .build();
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create()
// .setDefaultRequestConfig(defaultRequestConfig)
.setConnectionManager(connectionManager)
.evictIdleConnections(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// .disableAutomaticRetries() // 禁用自动重试
// 重试次数的设置需考虑超时时间
// .setRetryHandler(DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler.INSTANCE) // 在执行期间发生 IOException 之后是否应重试,自动重试没有禁用时,默认使用 DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler.INSTANCE
// .setRetryHandler(CustomHttpRequestRetryHandler.INSTANCE)
// .setServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy(new DefaultServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy()) // 是否根据响应重试
.setKeepAliveStrategy(new CustomConnectionKeepAliveStrategy()) // 默认使用 DefaultConnectionKeepAliveStrategy.INSTANCE(响应头有 Keep-Alive 则设置为其值,没有则永久有效)
// .disableCookieManagement() // 禁用 Cookie 回话保持功能,即不添加 RequestAddCookies、ResponseProcessCookies 拦截器,默认开启
// .setSSLSocketFactory(sslSocketFactory)
.setSSLContext(sslContext)
.setSSLHostnameVerifier(NoopHostnameVerifier.INSTANCE) // 关闭主机名验证
.build();
return new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpClient);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
// 自定义 KeepAlive 策略
public class CustomConnectionKeepAliveStrategy implements ConnectionKeepAliveStrategy {
private final long DEFAULT_SECONDS = 30;
@Override
public long getKeepAliveDuration(HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) {
return Arrays.stream(response.getHeaders(HTTP.CONN_KEEP_ALIVE))
.filter(h -> StringUtils.equalsIgnoreCase(h.getName(), "timeout")
&& StringUtils.isNumeric(h.getValue()))
.findFirst()
.map(h -> NumberUtils.toLong(h.getValue(), DEFAULT_SECONDS))
.orElse(DEFAULT_SECONDS) * 1000;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class CustomHttpRequestRetryHandler extends DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler {
public static final CustomHttpRequestRetryHandler INSTANCE = new CustomHttpRequestRetryHandler();
public CustomHttpRequestRetryHandler(int retryCount, boolean requestSentRetryEnabled, Collection<Class<? extends IOException>> clazzes) {
super(retryCount, requestSentRetryEnabled, clazzes);
}
public CustomHttpRequestRetryHandler() {
this(3, true, Arrays.asList(UnknownHostException.class, SSLException.class));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// 自定义服务响应重试策略
@AllArgsConstructor
public class HttpClientServerErrorRetryStrategy implements ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy {
private final int maxRetries;
private final long retryInterval;
@Override
public boolean retryRequest(final HttpResponse response, final int executionCount, final HttpContext context) {
return executionCount <= maxRetries
&& HttpStatus.Series.resolve(response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()) == HttpStatus.Series.SERVER_ERROR;
}
@Override
public long getRetryInterval() {
return retryInterval;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 使用 OkHttpClient
@Bean
public ClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory() {
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = null;
try {
// 导入客户端私钥 KeyStore
KeyManagerFactory kmf = KeyManagerFactory.getInstance(KeyManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("PKCS12");
keyStore.load(this.clientKeyStore.getInputStream(), clientKeyStorePassword.toCharArray());
kmf.init(keyStore, clientKeyStorePassword.toCharArray());
// 导入受信任的服务端证书 KeyStore
TrustManagerFactory tmf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
KeyStore trustKeyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
trustKeyStore.load(this.trustKeyStore.getInputStream(), trustKeyStorePassword.toCharArray());
tmf.init(trustKeyStore);
// 初始化SSL上下文
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
sslContext.init(kmf.getKeyManagers(), tmf.getTrustManagers(), null);
okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.sslSocketFactory(sslContext.getSocketFactory(), (X509TrustManager) tmf.getTrustManagers()[0])
.hostnameVerifier((hostname, session) -> true)
.retryOnConnectionFailure(true) // 失败重连
// .addInterceptor(new OkHttpRetryIntercepter(3, 1000)) // 延时重试拦截器
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Exception occurred!", e);
}
return new OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory(okHttpClient);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
@Slf4j
@Getter
public class OkHttpRetryIntercepter implements Interceptor {
private final int maxRetries;
private final long retryInterval;
public RetryIntercepter() {
this(1, 1000);
}
public RetryIntercepter(int maxRetries, long retryInterval) {
Assert.isTrue(maxRetries > 0, "Max retries may not be negative or zero");
Assert.isTrue(retryInterval > 0, "Max retries may not be negative or zero");
this.maxRetries = maxRetries;
this.retryInterval = retryInterval;
}
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
for (int proceedCount = 1; ; proceedCount++) {
try {
Response response = chain.proceed(request);
if (proceedCount <= maxRetries && HttpStatus.Series.resolve(response.code()) == HttpStatus.Series.SERVER_ERROR) {
long nextInterval = this.getRetryInterval();
try {
log.trace("Wait for " + nextInterval);
Thread.sleep(nextInterval);
} catch (final InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new InterruptedIOException();
}
} else {
return response;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (proceedCount <= maxRetries) {
log.warn("Http failed", ex);
} else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# RestTemplate 方法
- 11 种 HTTP 请求操作
exchange():在 URL 上执行特定的 HTTP 方法,返回包含对象的 ResponseEntityexecute():在 URL 上执行特定的 HTTP 方法,返回从响应体映射得到的对象getForEntity():发送一个 HTTP GET 请求,返回的 ResponseEntity 包含了从响应体中映射得到的对象以及响应相关的额外信息(如 HTTP 状态码和响应头)getForObject():发送一个 HTTP GET 请求,返回从响应体映射得到的对象postForEntity():POST 数据到一个 URL,返回的 ResponseEntity 包含了从响应体中映射得到的对象以及响应相关的额外信息postForObject():POST 数据到一个 URL,返回从响应体映射得到的对象postForLocation():POST 数据到一个 URL,返回新创建资源的 URLput():PUT 资源到特定的 URLdelete():在特定的 URL 上对资源执行 HTTP DELETE 操作headForHeaders():发送 HTTP HEAD 请求,返回包含特定资源 URL 的 HTTP 头optionsForAllow():发送 HTTP OPTIONS 请求,返回对特定 URL 的 Allow 头信息
- 大多数操作都以三种方法的形式进行了重载
T getForObject(URI url, Class<T> responseType):使用 java.net.URI 作为 URL 格式,不支持参数化 URLT getForObject(String url, Class<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables):使用 String 作为 URL 格式,并使用 Map 指明 URL 参数T getForObject(String url, Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables):使用 String 作为 URL 格式,并使用可变参数列表指明 URL 参数T postForObject(String url, Object request, Class<T> responseType, Map<String, ?> uriVariables)T postForObject(String url, Object request, Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables)T postForObject(URI url, Object request, Class<T> responseType)
- 注意:使用 String 作为 URL 格式的方法已经被假定 URL 字符串不被编码且需要编码
RestTemplate.HttpEntityRequestCallback#doWithRequest 方法会按消息转换器的装配顺序查找能转换 requestBodyClass、requestContentType 的 HttpMessageConverter,当没有指定请求头的 Content-Type 属性时,会设置 Content-Type 为该 HttpMessageConverter 响应的 MIME 类型中的第一种
# 发送 GET 请求
@GetMapping("accounts/filter")
public Account filter(String name, Integer age) {
return new Account();
}
public void getMethodTest() {
String url = "http://example.com/accounts/filter?name={name}&age={age}";
Account account = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Account.class, "libai", "26");
// Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
// params.put("age", "26");
// params.put("name", "libai");
// Account account = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Account.class, params);
// 等价于
/*ResponseEntity<Account> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, Account.class, params);
if (response.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful()) {
Account account = response.getBody();
}*/
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 发送 POST 请求
/**
* 使用 Payload 提交方式来提交数据
* Payload 提交方式与 Form 提交方式的区别
* Form 提交方式提交的数据,服务端可以通过 HttpServletRequest 类中的 getParameter(String) 方法获取
* 体现在 SpringMVC 框架中,即数据参数通过 @RequestParam 注解绑定获取
* Payload 提交方式提交的数据,服务端可以通过 HttpServletRequest 类中的 getInputStream() 方法获取
* 体现在 SpringMVC 框架中,即数据参数通过 @RequestBody 注解绑定获取
* 即本示例中 params 会被格式化成 json 格式数据,并放在 request body 中发送给服务端
*/
@PostMapping("accounts")
public Account create(@RequestBody Account account) {
return account;
}
public void postMethodTest() {
String url = "http://example.com/rest-server/accounts";
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("id", "100001");
params.put("name", "libai");
// RestTemplate 默认使用 Payload 方式提交数据,数据的格式是 json
Account account = restTemplate.postForObject(url, params, Account.class);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/**
* 使用 Form 提交方式来提交数据
* RestTemplate 默认使用 Payload 方式提交数据,想要使用 Form 方式提交,需要通过 HttpHeaders 设置
* 多个参数需要使用 LinkedMultiValueMap 来封装
*/
@PostMapping("accounts/create")
public Account create(Account account) {
return account;
}
@Test
public void postMethodTest2() {
String url = "http://example.com/accounts/create";
// 通过 HttpHeaders 设置 Form 方式提交
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
// 此处不能换成 HashMap
MultiValueMap<String, Object> form = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
form.add("id", "100001");
form.add("name", "libai");
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(form, headers);
Account account = restTemplate.postForObject(url, httpEntity, Account.class);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 发送带有 HttpHeader 信息的请求
@PostMapping("accounts/authorization")
public Account create(@RequestHeader("authorization") String authorization,
@RequestHeader("token") String token,
@RequestBody Account account) {
return new Account();
}
public void httpHeaderTest() {
String url = "http://example.com/accounts/authorization";
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("authorization", "12345678");
headers.add("token", "bce235emn97jjf00");
// headers.add(HttpHeaders.COOKIE,"key1=value1");
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("id", "10001");
params.put("name", "libai");
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(params, headers);
Account account = restTemplate.postForObject(url, httpEntity, Account.class);
}
public void httpHeaderTest2() {
URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl("http://example.com/accounts/authorization").build().toUri();
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("id", "10001");
params.put("name", "libai");
RequestEntity<Map<String, Object>> requestEntity = RequestEntity.post(uri)
.header("authorization", "12345678")
.header("token", "bce235emn97jjf00")
// .header(HttpHeaders.COOKIE,"key1=value1")
.body(params);
ResponseEntity<Account> response = restTemplate.exchange(requestEntity, Account.class);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# 文件上传
@Data
public class UploadReqDTO implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@NotNull
private MultipartFile imgFile;
@NotBlank
private String nickname;
}
@PostMapping(value = "accounts/logo", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
public Boolean changeLogo(@Validated UploadReqDTO reqDTO) {
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
@PostMapping(value = "accounts/logo", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
public Boolean changeLogo(@RequestPart("imgFile") MultipartFile imgFile,
@RequestParam("nickname") String nickname) {
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
public void fileUploadTest() {
String url = "http://example.com/accounts/logo";
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA);
MultiValueMap<String, Object> params = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
params.add("nickname", "nick");
// 方式一
params.add("imgFile", new FileSystemResource("D:\\abc.jpg"));
params.add("imgFile", new UrlResource("https://cdn.dida365.com/static/img/avatar-new.png"));
// 方式二
params.add("imgFile", new InMemoryResource("abc.jpg", "", FileCopyUtils.copyToByteArray(new File("D:\\abc.jpg")), System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 方式三
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="imgFile"; filename="logo.jpg"
// Content-Type: application/octet-stream
HttpHeaders imgHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
// mediaHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM); // 默认 application/octet-stream
imgHeaders.setContentDispositionFormData("imgFile", "logo.jpg");
byte[] bytes = FileCopyUtils.copyToByteArray(new File("D:\\abc.jpg"));
HttpEntity<ByteArrayResource> imgPart = new HttpEntity<>(new ByteArrayResource(bytes), imgHeaders);
params.add("imgFile", imgPart); // key 可以随机
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(params, headers);
Boolean result = restTemplate.postForObject(url, httpEntity, Boolean.class);
// Boolean result = restTemplate.postForObject(url, params, Boolean.class);
}
// 自定义一个 Resource 的实现类,用于上传数据流/字节数组
public class InMemoryResource extends ByteArrayResource {
private final String filename;
private final long lastModified;
public InMemoryResource(String filename, String description, byte[] content, long lastModified) {
super(content, description);
this.lastModified = lastModified;
this.filename = filename;
}
@Override
public long lastModified() {
return this.lastModified;
}
@Override
public String getFilename() {
return this.filename;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 文件下载
// 将下载文件一次性加载到本地内存,然后从内存将文件写入磁盘
// ResponseEntity<Resource> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(imgUrl, Resource.class);
ResponseEntity<byte[]> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(imgUrl, byte[].class);
if (response.getStatusCode().equals(HttpStatus.OK)) {
HttpHeaders headers = response.getHeaders();
// content-type/subtype,如 Content-Type: image/jpeg
headers.getContentType().getType();
headers.getContentType().getSubtype();
if (response.hasBody()) {
// Resource body = response.getBody();
// Content-disposition: attachment; filename="abc.jpg"
// String filename = body.getFilename(); // abc.jpg
// File file = new File("D:\\abc.jpg");
// FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(body.getInputStream(), new File("D:\\abc.jpg"));
// 打开指定的文件,如果父目录不存在,则创建该目录,如果文件不存在,将创建该文件
// try (OutputStream out = FileUtils.openOutputStream(file)) {
// FileCopyUtils.copy(body.getInputStream(), out);
// }
// byte[] imageBytes = FileCopyUtils.copyToByteArray(body.getInputStream());
byte[] imageBytes = response.getBody();
FileCopyUtils.copy(imageBytes, File.createTempFile("tmp-", "." + headers.getContentType().getSubtype()));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// 大文件流式下载
// 定义请求头的接收类型,APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM 表示以流的形式进行数据加载
RequestCallback requestCallback = request -> request.getHeaders()
.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM, MediaType.ALL));
// 对响应进行流式处理而不是将其全部加载到内存中
File file = new File(dir + File.separator + fileName);
restTemplate.execute(new URI(url), HttpMethod.GET, requestCallback, clientHttpResponse -> {
// 接收到一部分文件内容,就向磁盘写入一部分内容
// Files.copy(clientHttpResponse.getBody(), Paths.get(dir, fileName));
try (InputStream source = clientHttpResponse.getBody();
OutputStream out = FileUtils.openOutputStream(file, true)) {
IOUtils.copy(source, out);
}
return null;
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 处理有泛型类型字段的返回值
ParameterizedTypeReference<Result<XXX>> typeRef = new ParameterizedTypeReference<Result<XXX>>() {};
ResponseEntity<Result<XXX>> response = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.POST, httpEntity, typeRef);
1
2
2
# WebClient (opens new window)
Spring 提供的一个以 Reactive 方式处理 HTTP 请求的非阻塞式的客户端
支持的底层 HTTP 库:
- ReactorClientHttpConnector(Reactor Netty)
- JettyClientHttpConnector(Jetty ReactiveStream HttpClient)
创建 WebClient:
WebClient.create()、WebClient.Builder.build()发起请求:get()、post()、put()、delete()、patch()
获得结果:retrieve()、exchange()
处理 HTTP Status:onStatus()
应答正文:bodyToMono()、bodyToFlux()
Sponsor